Open RAN 5G & Open BTS 4G Online Training
Online Training
OPEN RAN 5G & OPEN BTS 4G
Open RAN is a technology that integrates all technologies, contains 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, in one server system. The core or server in Open RAN can be a virtual server, so that cellular operators can use multi vendors in implementing network topologies without being tied to one brand.
Open BTS is an alternative technology to build the own Base Transceiver Station (BTS) at an affordable price for GSM telecommunications based on open source software.
We’re offer you to join a Online Training about Open RAN 5G & Open BTS 4G, you will get a lots benefit! Check it out and enroll now!

Benefits join this Online Training :
What lessons will be learned in this Online Course/Training?
OPEN RAN 5G:
- Open RAN industry process
- Role map and concept of Open RAN
- How 5G works
- Challenges in existing industries and environment
- Open RAN architecture platform
OPEN BTS 4G :
- Concept around Open BTS
- How to configure software system for BTS
- Open BTS architecture platform
- Demonstration Open BTS
- Software and hardware supporting to develop BTS concept
Who this Online Course/Training is for?
This Online Course/Training Facilities :
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) :
Price :
(IDR) 750,000/participant
Testimonial Member :
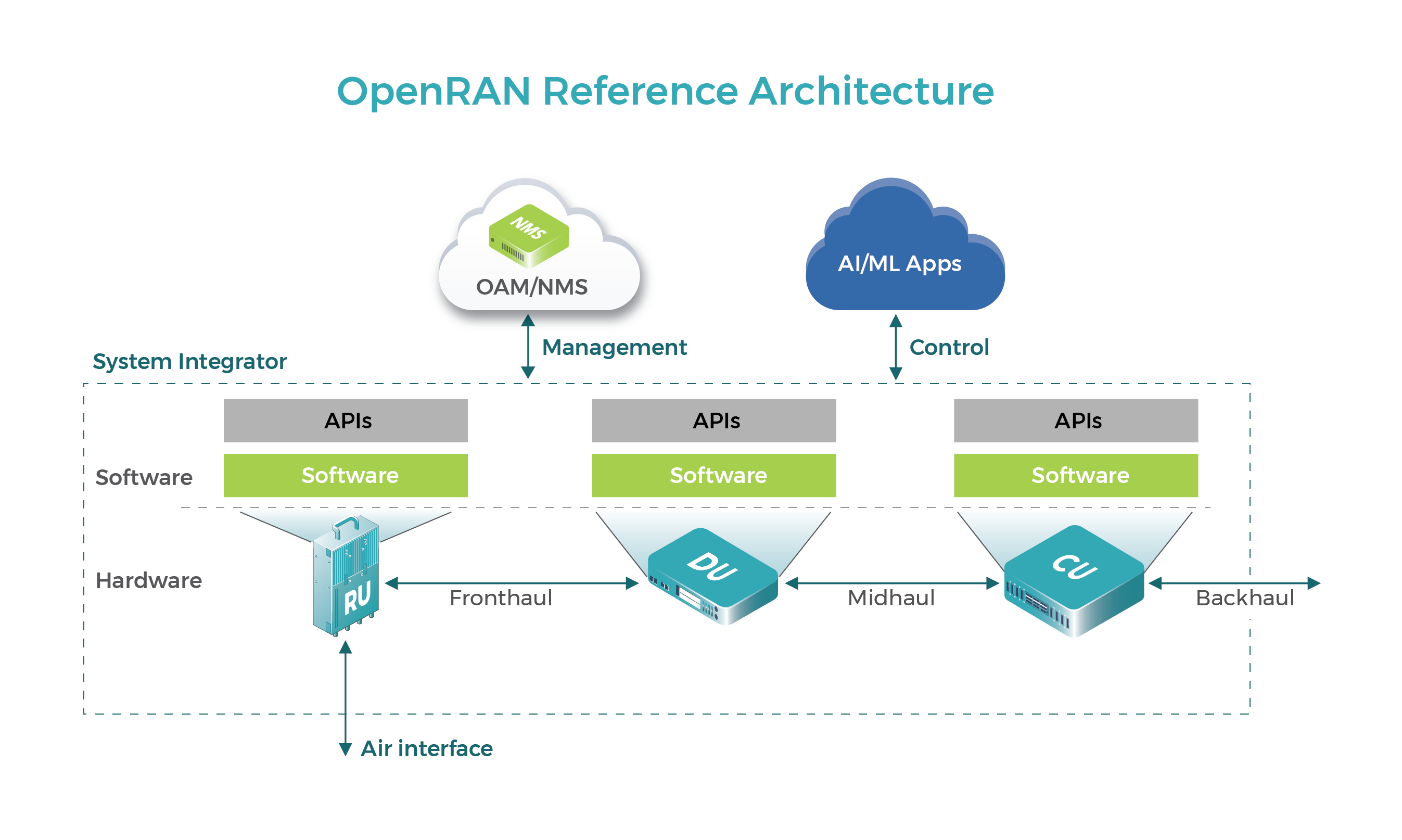
Why OpenRAN is A Game Changer for 5G Technology?
Introduction to OpenRAN
OpenRAN is an open and disaggregated radio access network concept. It is a complete and coherent software-based solution. It is an approach to solving a myriad of spectrum requirements using modularity, modularisation and open source. The mission is to provide all the functionality needed in a packet core and an IP client via a set of open reference implementations and modularisation to deliver a low cost 5G radio access network. OpenRAN provides a scalable open solution where the chipsets, devices, chipsets and components are selected and used on a cost effective and time optimized basis. The solution is made of a modular set of small cells. It is designed to cover all 5G use cases from high capacity to the tens of thousands of cells.
Socializing the OpenRAN Ecosystem
You may have several questions about OpenRAN wireless 5G network technology:
OpenRAN Benefits
The OpenRAN Concept: A Game Changer for 5G Technology
This training aims to:
Introduction to OpenRAN
Let’s begin from the basics, that is, an overview of what this new Ecosystem brings to the table. OpenRAN is an Ecosystem that promises faster innovation and quick time to market for mobile operators, who can easily and quickly find and integrate OpenRAN-ready solutions. It is built on standards that enable flexibility and interoperability across all stakeholders within the ecosystem. It enables networks to focus on what they do best: delivering quality of service, eliminating congestion, increasing flexibility, freeing bandwidth, making network upgrades more cost-effective and easier to execute.
Socializing the OpenRAN Ecosystem
The session will be organised in small group session for more effective and practical learning, because the group is designed to discuss and learn from each other. The venue is the 2018 Telco Innovation Summit (TIS) at Buenos Aires, Argentina, from 15 to 16 April 2018. There will be a one-day conference for CSPs, operators, developers and vendors to discuss the “State of Telco Innovation” and various topics such as 5G, Telco innovation, AI and IoT. The expectations from the Ecosystem Summit is to learn, share, discuss and discover the best innovative solutions in different vertical markets, governance and openness of the Telco Industry. The key message will be the benefits of OpenRAN Ecosystem and its impacts on the 4G/ 5G evolution.
OpenRAN Benefits
Conclusion
With such a strategy in place, operators can focus on enabling the delivery of enhanced wireless services, mobile broadband and cloud-based services on their mobile networks, with fewer distractions. This will help service providers establish themselves in new markets, attract new customers and expand their market share. The concept will also help create the ecosystem necessary to reach the requirements of the ubiquitous digital societies and open future 5G networks that 5G is shaping. In this way, operators can rapidly develop their end-to-end networks in the most cost-effective and efficient way.
What is an Open BTS 4G?
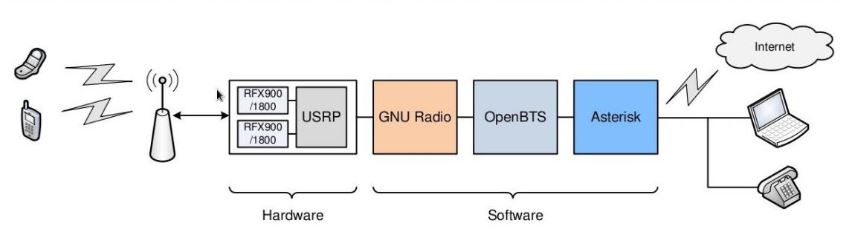
Introduction Open BTS
Open BTS is a BTS (Base Transceiver Station) application that runs on the Linux platform and is open software. Open BTS uses a piece of hardware called USRP (Universal Software Radio Peripheral). This device connects open BTS with the standard mobile phone network (GSM). Open BTS also uses open asterisk software to interconnect with other telephone networks such as PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) or other telecommunications operators using VoIP (Voice over IP). Open BTS is an open source platform for building a BTS (Base Transceiver Station) like a cellular operator’s network. The difference is that Open BTS is based on open source software, while commercial BTS owned by operators are hardware-based with the ITU-T protocol standard and are usually made by international vendors such as Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, etc.
What are the software that part of Open BTS?
Implementation technology of Open BTS
There are two main components to building a ‘cellular’ network based on Open BTS, namely hardware (USRP, antenna, duplexer, power amplifier) and software (Open BTS, Asterix, Jabber). USRP (Universal Software Radio Peripheral) is in charge of handling client requests through the air interface (Um), antenna as transmitter with 900/1800 Mhz band, duplexer is useful for dividing RF carrier into several sectoral antennas if desired and power amplifier to increase cellular coverage. The next supporting component is the software in charge of processing RF signals as a carrier based on DSP (Digital Signal Processor) and software in charge of processing data (softswitch, SMS handling, GPRS). DSP software in Open BTS is represented by DSR (Defined-Software Radio) whose job is to translate (decoding) signaling codes in data exchange and synchronization between BTS and client handsets.
Commercial version around Open BTS
Conclusion
A technology that is cheap but efficient certainly ‘threats’ the previous technology that was already established. OpenBTS is able to stand like a cellular operator network even with a smaller coverage scale but only requires relatively affordable installation costs. Thus anyone can set up their own ‘mobile operator’. This of course will cause problems for authorized operators, ranging from interference problems, decreased network performance to a decrease in revenue due to the habit of customers who are always looking for cheaper rates.
The tight competition in the telecommunications business in the country has prompted cellular operators to tighten their belts, but think hard so that network performance does not decrease. The commercial version of Open BTS seems worthy of consideration by cellular operators in Indonesia as an effort to develop cellular networks to remote rural areas, with lower CAPEX and OPEX costs but with quality equivalent to conventional GSM. With a few modifications, OpenBTS can also be used as a mobile BTS or a femtocell. Even migrating to IMS services is made easier using Open BTS.
